We live in an age of competition, where people are judged in their work environment by their effectiveness. Manager’s effectiveness is needed to make adequate production in any business. Being effective can reward now and throughout the career. Effective managers obtain attractive projects, win significant clients, and are well treated by their co-workers.
Effective Managers Skills
1. Taking ownership
An effective manager always takes ownership of all situations. He/she will never say that “it is not my fault.” Once a manager practices this trait, his/her team members will also follow it. This will result in producing a well-organized team.
2. Setting High Standards
To become a successful manager, one needs to set high standards. A manager should not settle for anything but the best. So, it is essential to plant high standards at the beginning of the project itself. Settling only for the best will lead to high-yielding results.
3. Focus on Improvement
Exemplary managers will always focus on improving, and they will never settle. Even at the age of fifty or sixty, a manager must find numerous ways to improve his/her managerial skills—he/she must read books like Extreme Ownership by Jocko Willink, Highly Effective People, and Primary Leadership.
4. Listen More, Speak Less
“The smarter you get, the more you listen, and the less you say”, which portrays the habit of an effective manager. Listening enables a manager to understand better in a professional surrounding. It allows building a stronger relationship with the team members.
It will, in turn, will enable the manager to identify the strength and weaknesses of the team members individually. Moreover, listening pulls in knowledge and information.
5. Building Relationships
A great manager must build a supportive relationship in the workplace. This trait will make the work environment enjoyable and productive. Constructing a good relationship with the team members will insert confidence in them.
As a result, they will start to feel voicing opinions, brainstorming, and empowers the team to change, create and innovate. A robust professional circle will offer freedom, career development, and opportunities.
A quality workplace relationship needs accessible communication, respect, involvement, and trust. A supportive team will always be helpful, even in a critical situation.
6. Sometimes, Do Nothing
More often than you think, doing nothing can be the smartest thing to do. People might think that to be an effective manager, one must make decisions all the time, but this is not true. A good manager must always ask himself, “should I make a decision right now?” To produce complete managerial skills, one must make a decision only when it is necessary.
7. To Master the Art of Filtering
A manager must always filter ideas. Therefore, he/she should first draw up a list of things that are needed and prioritize the most crucial things, and the rest can be done later.
8. Understand the Employees
A potent manager must get to know their employees. Even if his/her team consists of five members or fifty members, the manager is responsible for understanding his/her employees. This will allow the manager to pinpoint the efficiency of the team members. Therefore, he/she can allocate appropriate works to the employees depending upon their skills.
To understand the team members, the managers must move comfortably with the team. On the other hand, spotting the weaknesses of the team members can help them improvising. Providing effective training, coaches, and mentors will make them feel valued and appreciated. It is also crucial to know their aspirations.
Praise them when they do a good job. This will insert confidence and drive them to do future works more interestingly. Providing honest feedback will enable them to push their career to high standards.
9. Seek Feedback
High-ranked managers should ask for feedback. Feedback is a silent feature of effective learning solutions. Following the feedback causes the manager to pause, engage, and modify their managerial skills. It is also crucial that one must not act accordingly to all the feedbacks.
10. Making Decisions Not Based on Emotion
Most times, emotions lead to bad decisions. Often people make decisions on the verge of their overflowing emotions. This can be very dangerous in the workplace. An effective manager must think and act.
Therefore, he or she must pay attention to their feelings and emotions. Emotions mostly alter one’s behavior and thinking.
11. Have a Mentor
Having someone to guide and help will enable a manager to learn and grow faster. Always keeping an experienced person will upgrade the manager’s work. A mentor can furnish practical advice, support, encouragement, develop, and studies a manager’s communication and personal skills.
Essential Manager Effectiveness Metrics
Metrics are measurements that deliver insights on advancement towards attaining a business goal. It can also be called Key Performance Indicators (KPIs). Matrix helps in different outlines. It largely depends on the financial analysis of the company by external stakeholders and internal managers.
#1 Performance Metrics
One of the prominent metrics is the performance of the team. It includes the code, conduct, and systematics of the team members. Performance metrics are degrees of metrics given by a team, business, or individual.
Some of the examples of performance metrics are listed below:
- Customer Satisfaction
- Deform/Defect Density
- Schedule Variance
- Budget Variance
- Quality
- Volume
- Turn-around time
- Waste
- Efficiency
- Productivity
- Cost-effectiveness
- Revenue Per Employee
- Return on Capital Employee
#2 Transformation/Innovation
An effective manager’s managerial metrics can also be calculated by the innovation and the amount of contribution, and the rate of alteration on his/her goals. Innovation is a kind of methodology used to check the innovation efforts of an organization. You can consider it as one of the most challenging tasks. Being a powerful and firm competitor is the objective of innovation.
The factors of innovation metrics are listed below:
- Cost Improvement Rate
- Developmental Line
- Experiment Cycle Time
- Experiments
- Growth Gap
- Idea Breadth
- Idea Depth
- Idea generation
- Idea Selection
- Innovation Compensation
- Innovation Overhead
- New Patents
- New Products
- New Revenue Rate
- Project Risk
- Return on Investment
- Sustainability Metrics
- Time of Market
- Time to volume
#3 Procedure and Processes
The procedures and processes are the major factors that decide the final quality and quantity of an organization. It is often measured by management accounting. Management accounting is stuffed with both financial and non-financial problems. It is slightly different from financial accounting.
The elements of management accounting are:
- Activity-based costing
- Baseline
- Benchmarks
- Cycle Time
- Cost to company
- Cash Cycle
- Rate of Complexity
- Limits of Contribution
- Analysis of Cost-Benefit
- Target Costing
- Ownership Cost
- Qualification
- Run Rate
- Rate of Productivity
- Formula Productivity
#4 Project Metrics
It is a method used to measure projects. Mainly, they provide ideas and direction to govern the ongoing projects. They also look at whether the projects are set on time and account limit. Risk is the secondary factor of project metrics.
The following are project metric indicators:
- Real Cost
- Error Solution Rate
- Cost Differences
- Consistency of Design
- Occurred Value
- Estimate to Complete
- Approximate Time to Complete
- Milepoint Achievement
- Payback Duration
- Project Velocity
- Asset Utilization
- Risk Manifestation
#5 Quality Metrics
Quality metrics measure quality checks and ratings for the product. This predominantly produces a good opinion on the organization. It will undoubtedly increase the manager’s effectiveness and boost his/her team member’s confidence level.
Examples of quality metrics:
- Customer Satisfaction
- Rating
- Failure Rate
- Mean Time Between Failures
- Service Quality
- Quality Control
- Rate of Error
#6 Risk Management
Risk management examines the work that indulges in risk management processes.
The techniques of risk management are:
- Risk Capacity
- Risk Evaluation
- Risk Identification
- Risk Impact
- Risk Exposure
- Risk Perception
- Risk Matrix
- Cost of Risk
- Hazard
Manager Effective Index
Manager effective index has been introduced to examine a manager. It promotes a manager into an eminent leader. There are specific ways to identify the Manager Effective Index.
- Locating the prominent habits of effective managers at an organization.
- Changing the conventional performing methods.
- Indulging employees in the manager’s development plans.
How to Become an Effective Manager?
People would have worked in various organizations throughout their careers and under different manager’s managerial roles. From all those years, they can easily spot out the ones who were excellent and exemplary.
#1 Stop Committing Blunders
A good manager should never committee a blunder in his profession. He/she must remember that they are no more an employee but a person who is set to manage their team.
#2 No Spoon-Feeding Remedies
To become an effective manager, one must not supply everything on their employee’s plate. Instead, they should make their employers find solutions to the problem. It will refine the team members’ activity and make them think.
Spoon-Feeding technique will not allow the employees to work effectively on their own.
#3 Define Your Goals
It is very crucial to set goals for a noteworthy manager. One must set goals even for a small-scale project. Failing to define goals will showcase harmful production. Therefore, as a manager, he will create a second-class impression on his employee’s mind.
- Grades of Good Manager
- Lining Up Company Motive Along with the Team Members.
- Exhibiting Empathy with the Team.
- Confining Work Effectively.
- Positioning Distinct Aims and Expectations.
- Prioritizing Communication.
- Recognizing the Best in Employees.
- Holding the Latest Technology.
- Raising Team for Success.
- Inclining at Every Level.
- Open to Learning.
- Domain Knowledge
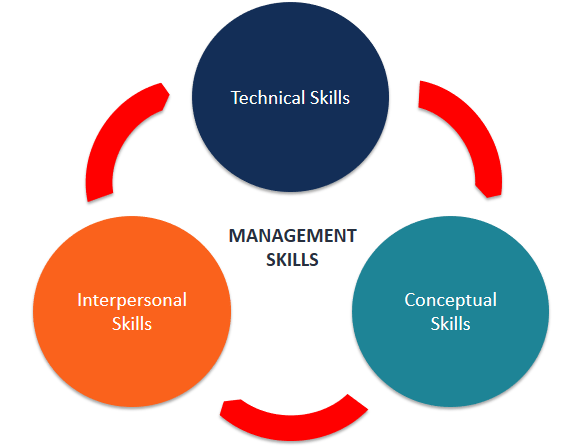
Managerial Skills
- Practical Skills: A manager must possess valuable skills in all perceptions. He must be very proficient in technical knowledge.
- Intellectual Skills: This States the potential to synchronize and merge the project task in management.
- Good Governing Skills: A refined manager must know to act right in all situations. Even a tiny mistake will cause negative marking in productivity.
- Communication Skill: Communication skill is a fundamental skill for a manager. A proficient manager must deliver thoughts, knowledge, and information to the employees.
- Diagnostic Skills: A manager must have the capacity to analyze the most pleasing response in any situation.
- Leadership Skills: Leadership is the ability to convert vision into reality. A good leader will always make a proper team. Therefore, a manager must lead effectively. Effective managers will encourage their team to do noble deeds.